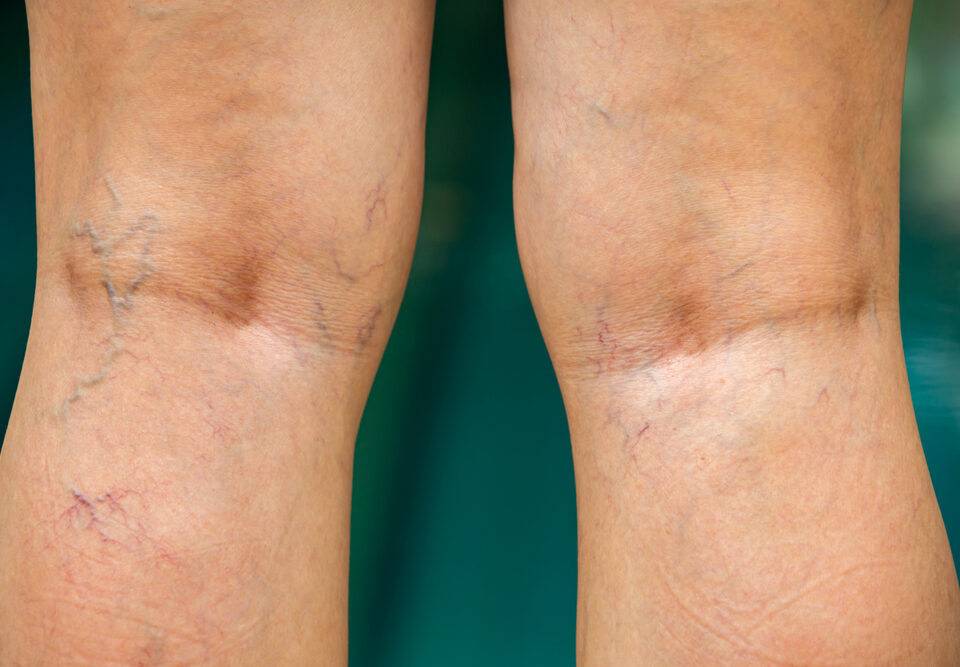
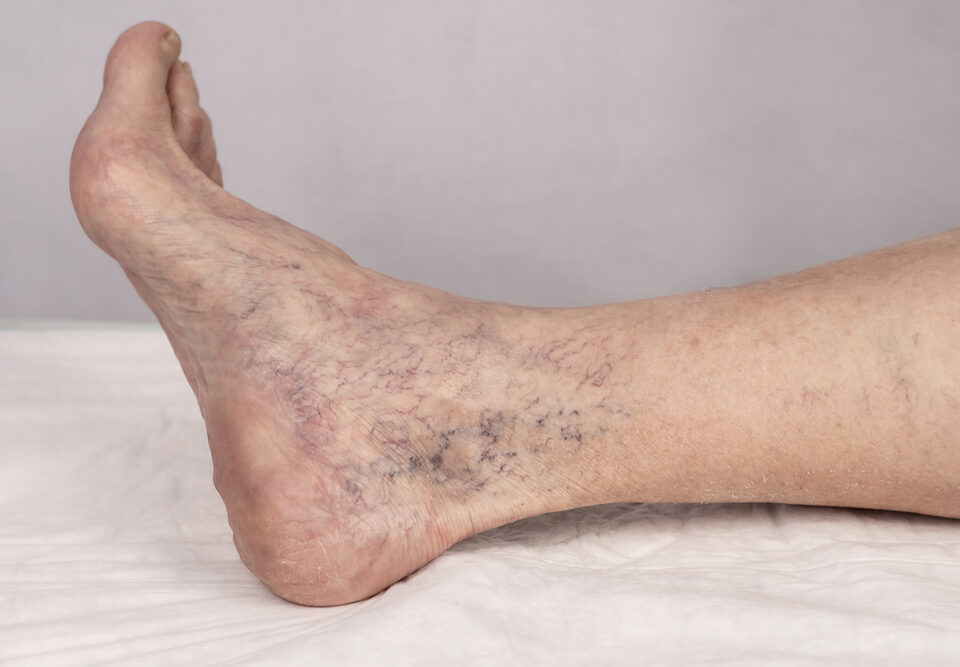
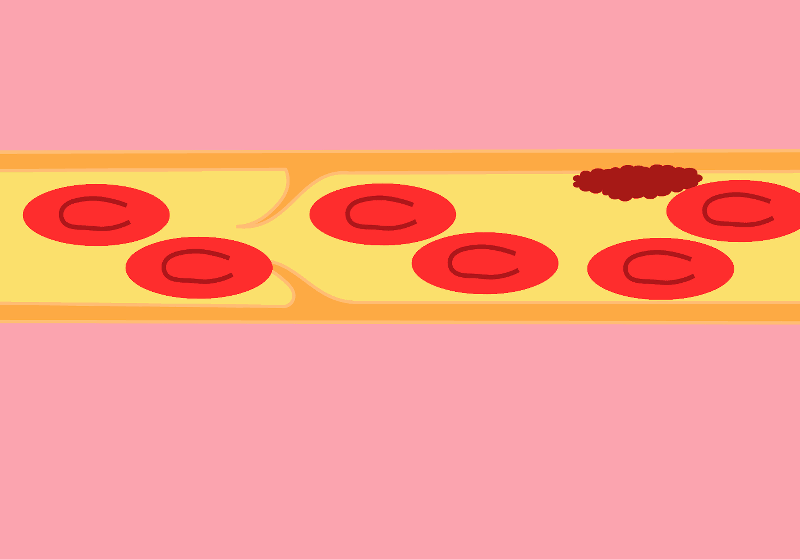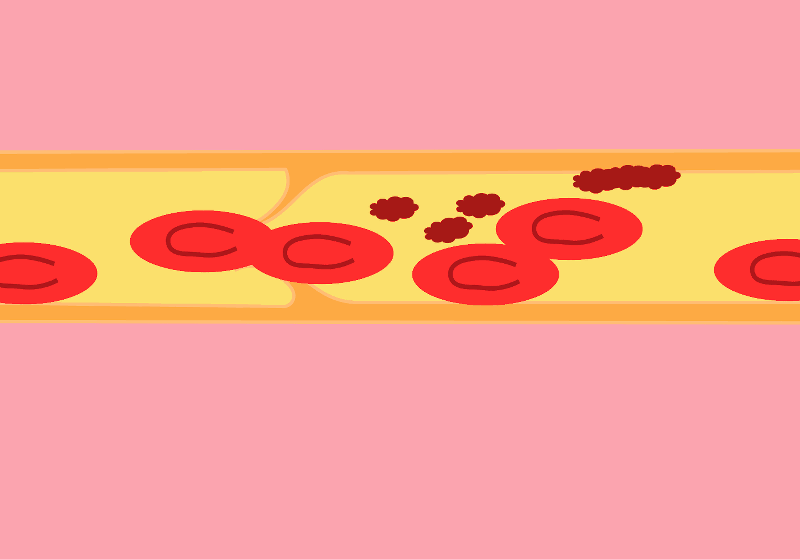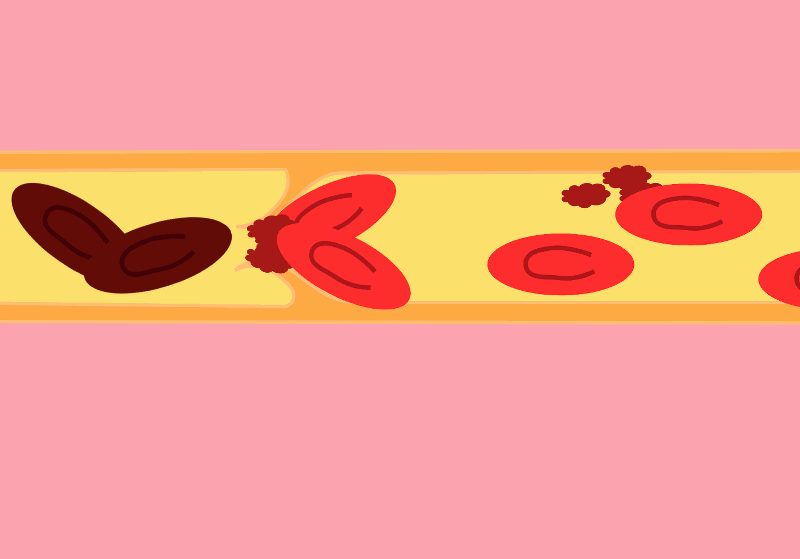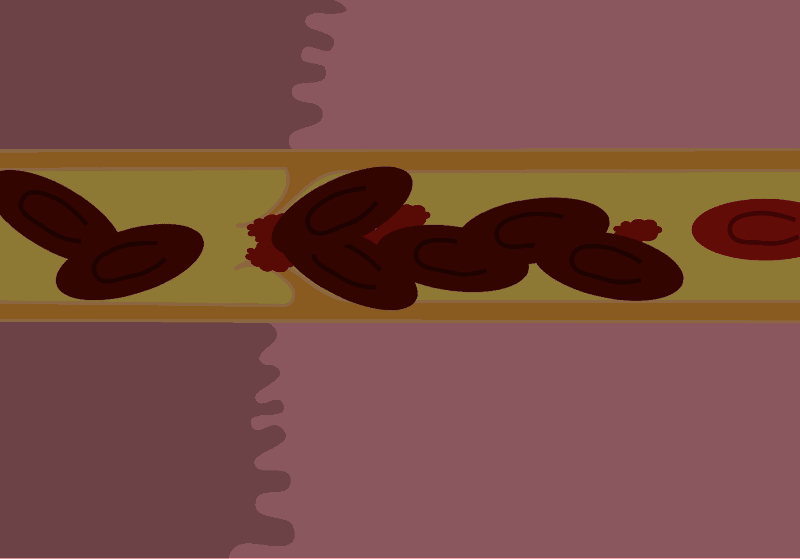
When a blood clot, also known as a thrombus, forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, this can lead to the development of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT most often occurs in the legs, which has the highest concentration of veins susceptible to thrombus formation. The condition can present no symptoms at all, or can manifest with leg pain or swelling. Certain medical conditions can also cause DVT, especially if they affect how your blood clots.
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious concern. The blood clots sitting in your veins can break loose from the arterial walls. From there, they will travel through the bloodstream and lodge in your lungs or heart, blocking blood flow and leading to a pulmonary embolism.
Signs and Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Swelling in the affected leg
- Pain in the affected leg, often staring in the calf. Sometimes feels like cramping, or soreness
- Discolored, red skin on the leg
Be sure to see a doctor if you develop signs or symptoms of DVT. Seek immediate medical attention if you detect signs of a pulmonary embolism. These include:
- A sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain that gets worse when you take a deep breath
- Dizzy spells or fainting
- A rapid pulse that doesn’t go away after a short while
- Coughing up blood from the lungs
Risk Factors for Deep Vein Thrombosis
- An inherited disorder – some people can inherit a disorder from their parents that makes their blood clot more easily, but this on its own may not be enough to cause the clots endemic to DVT without other risk factors
- Prolonged bed rest or paralysis – if your legs remain still for extended periods of time, such as lying in bed after another medical procedure, your calf muscles don’t stimulate circulation by contracting
- Injury – injuries that cause damage to blood vessels and internal bleeding can leave permanent damage that increases the risk of blood clots
- Pregnancy – the changes in the body resulting from pregnancy increases pressure on the veins in the pelvis and legs
- Birth control pills – some medications have side effects that increase the risk of blood clots
- Smoking – nicotine affects circulation
- Being overweight or obese
- Inflammatory bowel diesease (IBD)
- Age – though DVT can occur in any age, being older than 60 increases the risk exponentially
Deep Vein Thrombosis Prevention
- Avoid sitting still for long periods of time – if you are recovering from surgery, or have been prescribed bed rest for other reasons, be sure to at least stand and move around the room every once in a while to stimulate blood flow in your legs. Don’t cross your legs while sitting for long periods, as it hampers blood flow. Take breaks on long road trips to stand and walk around.
- Make lifestyle changes – incorporate more physical activity into your daily routine to lose weight and improve cardiovascular health. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your circulatory system.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment
- Blood thinners – The most common treatment for DVT is blood thinners, or anticoagulants. These drugs decrease your blood’s ability to clot, and can be injected or taken as pills. Be sure to take these exactly as your doctor instructs, as any wavering from the prescribed amounts can cause serious side effects.
- Clot busters – While anticoagulants are aimed at reducing the risk of clots forming, clot busters (also known as thrombolytics) are drugs designed to actually break up existing clots. They are given through an IV line or catheter directly into the clot to dissolve it.
- Compression stockings – These are worn on your legs to prevent the swelling that results from DVT.
- Catheter
- Surgery
For more information, please contact the vascular and cardiology healthcare professionals at Premier Vein & Vascular by calling 1-888-VEINCARE or use our convenient online form to request an appointment. We look forward to serving you at our offices in Tampa and Largo, Florida.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
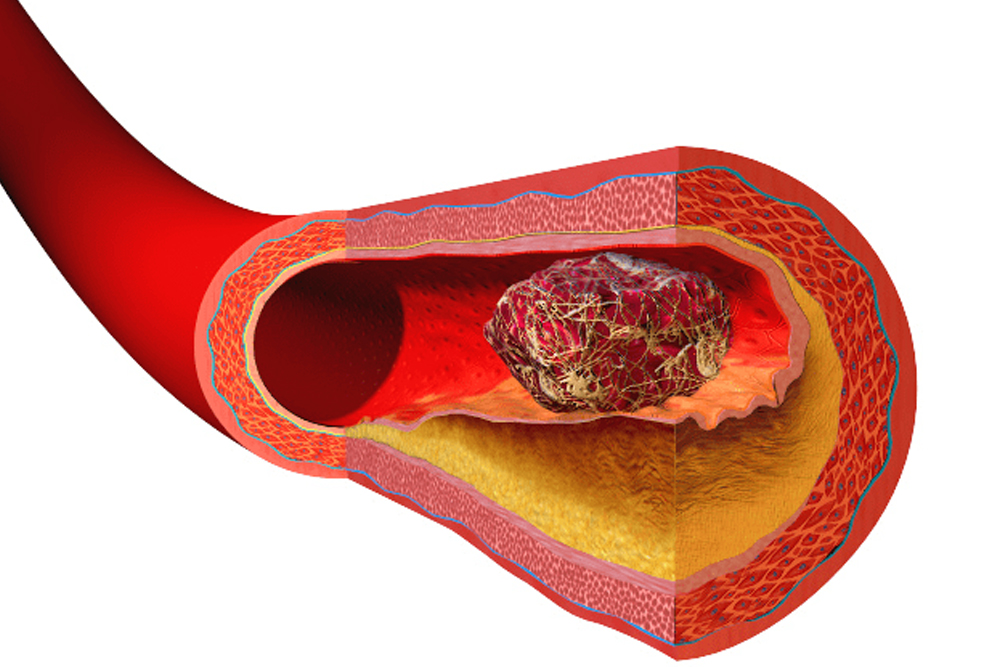
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot develops in the large, deep veins of the pelvis, legs, thighs, or arms. This is a serious condition in which a deep vein – one that cannot be seen – becomes partially or completely blocked by a blood clot (thrombus), which forms …


 Premier Vein & Vascular
Premier Vein & Vascular