Deep Vein Thrombosis
Premier Vein & Vascular
Vascular and Endovascular Surgery located in Tampa, FL & Largo, FL
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a common blot clotting condition, with nearly 300,000 Americans developing a deep vein clot for the first time each year. DVT doesn’t always have noticeable symptoms, but it can trigger a life-threatening pulmonary embolism if left untreated. Get screened and stay healthy at Premier Vein & Vascular. With two locations in Tampa and Largo, Florida, Nestor Guerrero, ARNP-C and the team are here to help you understand your risk for DVT and get effective treatment. Call the nearest office for an appointment or book online today.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Q & A
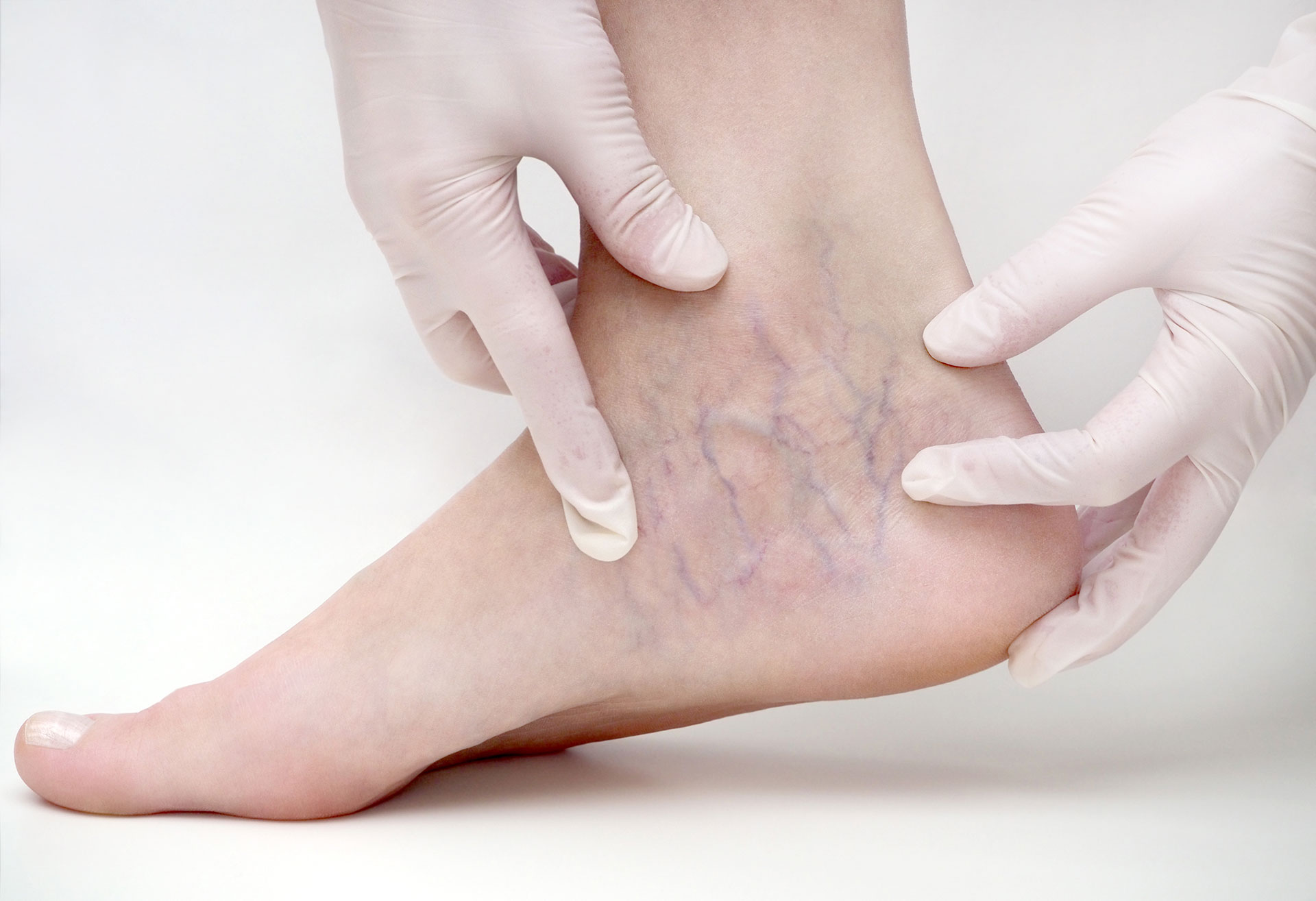
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that develops when a blood clot, or thrombus, forms inside a vein deep in your body. It’s most common in the legs, but it’s possible to experience DVT in the pelvis or arms.
DVT is a serious medical condition. The blood clot that forms partially or completely blocks blood flow, and it can become life-threatening if the clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs. A clot that blocks blood flow in the lungs can cause a pulmonary embolism.
People who have blood clotting disorders or who are inactive for long periods of time are at risk for DVT. Smoking, being overweight, and certain other factors may increase your risk, too.
When a blood clot breaks free from a vein in your leg, it can travel to your lungs. Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a life-threatening complication that can develop when a clot blocks blood vessels inside your lungs.
Symptoms of PE include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rapid pulse
- Coughing up blood
If you notice signs of PE in yourself or a loved one, seek immediate medical care.
Symptoms of DVT may include leg pain, a feeling of warmth, or skin discoloration, but symptoms aren’t always noticeable. If you have a blood clotting disorder or if you go long periods of time without moving, you could be at risk for DVT.
There are a number of tests offered at Premier Vein & Vascular to diagnose DVT before it develops into a life-threatening pulmonary embolism.
D-dimer blood test
This simple blood test assesses the presence of large, dangerous clots. The test measures the D-dimer levels, a protein fragment that’s left behind in your blood when a blood clot breaks down. High amounts of D-dimer may indicate DVT.
Duplex ultrasound
An ultrasound to screen for DVT involves using soundwaves to create images of your veins. Duplex ultrasounds, also called vascular ultrasounds, measure blood flow through veins to determine speed and rule out blockages.
Venography
In a venography, a special dye is injected into your leg veins and viewed with X-ray. If blood flow is slower than normal, it’s evident during the test. Venography is generally recommended if other tests are inconclusive.
Blood thinning medications, or anticoagulants, are an effective treatment option for many people with DVT. Blood thinners reduce the risk of clots forming inside your veins. Be sure to take the medication exactly as prescribed, because taking too much or too little can cause complications.
Blood thinners don’t break up clots that already exist, but they can keep them from getting larger. Most clots dissolve on their own in time. If you have existing blood clots, talk to the team at Premier Vein & Vascular about ways to reduce your risk of PE.
Find top-quality care for deep vein thrombosis at Premier Vein & Vascular. To understand your risk factors and learn what you can do to stay healthy, book your appointment online or over the phone today.

